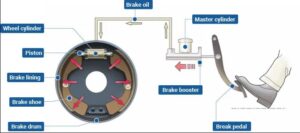
Wheel Cylinder Function

the Wheel Cylinder is the Second important Component Of the hydraulic Brake system.
It Consists of the piston which can move in opposite directions by the fluid pressure. It is Rigidly mounted on the Brake Shield or Backing Plate. The Boots Protect the cylinders from Foreign Substance. Bleeder Valves are Provided in the Cylinder to permit air and liquid to pumped out of the System During the bleeding operation
piston Cup fits tightly in the Cylinder against each piston and seal the mechanism against leakage of the brake Fluid. a spring serves to hold the cup against the piston when the pressure is decreased.
When the brakes are applied the brake fluid enters the cylinder from a brake line connection inlet between the two piston it cases to force wheel
This is a part of a hydraulic fluid is driven drum brake system and is situated in each wheel. Mainly the cylinder is situated at the top of the wheel, above the shoes. It is very much like a slave cylinder and works similarly, inside comprising of just a basic plunger. On older cars these may start to leak and limit the performance of the braking system yet are regularly cheap and generally simple to replace. You can contact your local car garages for a better understanding.
The wheel cylinder comprises a cylinder that has two pistons, one on each side. Every cylinder has an elastic or rubber seal and a shaft that interfaces the cylinder with a brake shoe. At the point when brake pressure is applied, the cylinders are constrained out driving the shoes into contact with the drum. A few plans utilise two single-piston wheel cylinders, one at the top point of the drum and one at the base, each associated or connected with one brake shoe.

A wheel cylinder has the following components inside:
- Two pistons on each side
- Two rubber cups on each side
- Spring in the middle of the pistons
The fluid squashes against the pistons that move outward in the wheel cylinder at the point when the pistons come nearer. This is when the fluid is constrained into the master cylinder, the spring between the two pistons holds the elastic cups in position.

Wheel cylinders are now made from aluminium as previously they used to be made of cast iron. However, they were more prone to rusting.
A wheel cylinder is a component of a hydraulic drum brake. The wheel cylinder must force apart the brake shoes and press them against the brake drum. This generates friction and the wheel is decelerated. This happens every time the driver presses on the brake pedal. Pressing on the brake pedal generates a hydraulic pressure in the master brake cylinder which is transmitted to the wheel cylinder in the brake fluid via the brake lines. In the wheel cylinder, the hydraulic pressure acts on the pistons, which then exert mechanical pressure on the brake shoes.
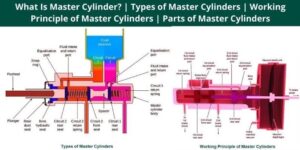
the master cylinder is the Heart Of the hydraulic brake system. a master cylinder in hydraulic braking system is an intermediate component that worked as an energy converter as well as force multiplier i.e. mechanical energy into hydraulic pressure so we need master cylinder in hydraulic braking system
It Consists of two main chambers. Fluid Reservoir and compression chamber.
1) The compression chamber in which the piston operates
2) the Fluid Reservoir which contains the fluid to supply to the brake system. the reservoir Supplies fluid to the brake system through two ports
- The larger port is called the filler or intake Port and is connected to the hollow portion of the piston between the primary and secondary cups which act as piston seals.
- The smaller port is called the relief , Bypass or Compensation port which connects the reservoir to the atmosphere so that the atmospheric pressure causes the flow through the filler port . the vent is placed in the filler cap. the boot covers the push rod and the end of the cylinder to keep it free from foreign matter.
When the Brake Pedal is Depressed the master cylinder piston moves Forward to Force the Liquid under pressure into the system the relief port is sealed out of the system the liquid pressure is conducted to the wheel cylinder where it force the wheel cylinder piston outwards. these pistons force the brake shoes out against the brake drums.
Types of Master Cylinder
1. Single Circuit Master Cylinder
2. Tandem Master Cylinder or Dual Circuit Master Cylinder
Single Circuit Master Cylinder
- In single circuit master cylinder when brake pedal is not pressed i.e. non actuation position the piston remains at its original position which in turn closes the inlet valve of the reservoir due to which there is no incoming of brake fluid takes place between reservoir to compression chamber.
- When brake pedal is pressed i.e. actuated position, the piston which is connected to the brake pedal through connecting rod moves which in turn opens the inlet valve due to which incoming of brake fluid from reservoir to compression chamber takes place.
- This brake fluid inside the compression chamber is compressed due to the movement of piston inside the cylinder just like the medical syringe.
- After compression up to a certain pressure the outlet valve opens and this highly compressed brake fluid is further transferred to the brake lines for further brake actuation.
It consist of 5 parts

1. Reservoir
It is the storage tank used for storing the brake fluid in hydraulic type of braking system, usually it is made up of plastic.
2. Cylinder
It is the air tight housing inside which the piston moves with the moment of brake pedal which in turn causes conversion and multiplication of force. Cylinder is usually made up of cast iron or aluminum.
- It is connected with the reservoir through inlet valve and also with brake lines through outlet valve.
- In single circuit m c there is only 1 compression chamber.
3. Piston
It is the reciprocating part of the master cylinder that reciprocates inside the cylinder due to the movement of brake pedal, the piston causes compression of brake fluid inside the cylinder which in turn generates high hydraulic pressure.
- In single circuit only 1 piston is used.
4. Returning Spring
It is the simple coil type of spring used inside the cylinder which helps the piston and brake pedal to retain its original position after brake pedal is released.
5. Valve
In single circuit m c it is the outlet valve through which the brake line is attached, The compressed brake fluid is further transferred to the caliper through this valve.
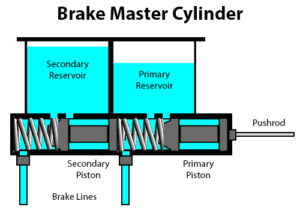
Tandem Master Cylinder
- When brake pedal is not actuated, the piston remains at their original place, closing the inlet valve of both the compression chambers, which in turn cuts the incoming of brake fluid between both the reservoir or both the reservoir chambers.
- When the brake pedal is actuated, at first the primary piston moves due to which opening of primary inlet valve takes place.
- Initially due to the movement of primary piston compression of the brake fluid inside primary chamber takes place.
- After completion of the compression in primary chamber primary outlet valve opens up and this compressed brake fluid is further sent to brake callipers through brake lines and actuation of the primary circuit brakes take place.
- After the completion of the primary piston movement i.e. at its extreme end, the secondary piston starts moving because of the force applied by the primary piston’s spring which in turn opens the secondary valve and incoming of brake fluid from secondary reservoir to secondary compression chamber takes place.
- This brake fluid is then compressed and after complete compression secondary outlet opens up and this highly compressed fluid is sent to the brake callipers through brake lines and actuation of the secondary circuit brakes take place.
1. Reservoir
In tandem master cylinder instead of single reservoir 2 or dual chamber reservoir is used as a storage tank for brake fluid.
2. Cylinder
Same cylinder as in single circuit type is used with the little modification i.e. it is the housing of 2 pistons and also there are 2 outlet and 2 inlet valves.
- In tandem m c there are 2 compression chamber inside the cylinder.
3. Piston
Instead of one piston, 2 pistons that are primary piston and secondary piston are used in tandem m c, the actuation of secondary piston occurs after completion of the primary piston movement.
- primary piston is connected to the brake pedal and secondary piston is placed just behind the returning spring of primary piston.
4. Returning Spring
In tandem m c 2 returning springs are used one with the primary piston and second with the secondary piston.
5. Valves
In tandem master cylinder as it is the dual circuit m c , 2 inlet and 2 outlet valves are used .
FAQ
What Is A Wheel Cylinder?
The brake wheel cylinder is a key component of your car’s drum brake system.
It’s positioned at the top of the wheel inside the drum brake and is mounted to the drum brake backing plate with a bolt.
What is it used for?
It’s used to push a pair of brake shoes outwards so that they can contact a brake drum to slow down your vehicle with friction.
How is this different from a disc brake?
Unlike the drum brake wheel cylinder that delivers a pushing force onto a brake shoe, a disc brake caliper squeezes a brake pad onto each side of a spinning rotor to slow the car down.
How common are drum brakes?
While most modern vehicles use disc brakes, it’s still common for an older car or a small truck to still have drum brakes on their rear tires.

[…] Cylinder […]
[…] Cylinder […]
[…] Cylinder […]
[…] Cylinder […]