photo credit by 123rf
Brake system: The vehicle Has to move on varying road conditions of traffic inclined up and down curved path etc. for this vehicle should have to be controlled properly. The brake system is one of the important controlling systems. Brakes are employed to stop or slow down the speed of the vehicle. Brake applied to the wheel braking force is created that force is created that force opposes the speed of the wheel or rotation of force. The kinetic energy of the motion of the Vehicle is transformed into heat generated by the Friction between the lining and The rotating Drum. The heat generated is dissipated into the surrounding air.
Main Function Of Brake System
- Control the driving of the Vehicle
- IT Stop the Vehicle and slows Down the Speed of the vehicle
- It must have strong braking farce
- It Must operate easily
Brake System Are of Two Types
-
Parking Brake ( Emergency Brake)
-
Service brake (Main Brake)
In case Of facture of service Brake we may use parking Broke For the time being as emergency
Parking Brake:- It is used to hold the vehicle stationary, when applied at the time of parking the braking is necessary to prevent the vehicle from enrolling off due to road gradient or blowing wind the brake manually operates on the rear wheel through cables or mechanical linkage from an auxiliary foot lever . it is held on by a ratchet until released by some means such as a push button or a lever
Service brake;- the most automotive service brakes are Hydraulic Brakes The Hydraulic Action Begins When Force Is applied to the Brake pad. this Force Creates Pressure in the master cylinder , either directly or though a power booster. it serves to Displaced Fluid transmits the pressure through the fluid Filled Brake Lines to the wheel Cylinder that Actuate the brake shoe. the Actuation of these mechanisms force the brake pads and lining against the rotors ( from Wheel) or Drums to stop the Wheels
Different Types of Brake System
-
Mechanical Brake
-
Hydraulic Brake
-
Power Brakes
1) Mechanical Brake :- Mechanical Brake is Used for Light Vehicle. the wheel is attached to an auxiliary wheel called Drum. the brake shoes are made to contact this drum. mainly in bike Moter Cycle Scooter In this type of brake system power in transmitted through mechanical linkage From Brake paddle to the brake Shoes to Actuate on brake Drum on Wheel rim
2) Hydraulic Brake SYSTEM :- the hydraulic brakes are applied by the liquid pressure. the pedal Force is transmitted to the brake shoe by means of a confined liquid through a system of force transmission the Force applied to the pedal is multiplied and transmitted to all the brake shoes by a force transmission system. this system is based upon pascal’s low which state that the confined liquid transmit pressure without loss equally in all direction. In most of the Vehicle Hydraulic Brake System is used Hydraulic Brake System Work on Pascal’s Low
PASCAL LOW According to this Low it non-Viscous in Compressible Liquid is kept in a closed vassal and some pressure is applied in it any one side it would be equally transmitted in all direction it out diminishing
Hydraulic Brake System it essentially consist of two main components master cylinder and wheel cylinder.
3) Power Brakes:- The braking System
- Air Brakes
- Air Hydraulic Brakes
- vacuum brakes
- Electric brakes
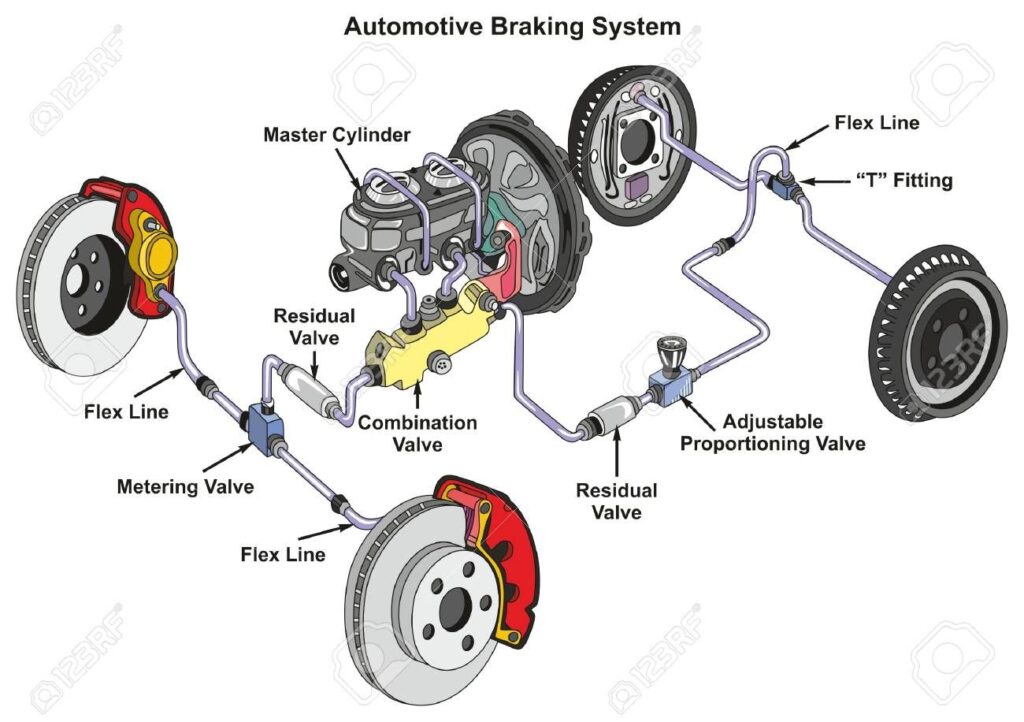
Parts Of Brake System
Following are Parts of the brake system:
- Brake Pedal
- Master Cylinder
- Brake Pads
- ABS Control Module
- Brake Booster
- Disc Brakes
- Drum Brakes
- Emergency Brake
- Brake Pedal
- Wheel Speed Sensors
1. Brake Pedal
The pedal is what you push with your foot to activate the brakes. It causes brake fluid to flow through the system to put pressure on the brake pads.
Driver steps on the brake pedal to activate the brakes. A piston in the master cylinder moves when the pedal is pressed.
2. Master Cylinder
The master cylinder is basically a plunger that is activated by the brake pedal. It is what holds the brake fluid and forces it through the brake lines when activated.
Converts non-hydraulic pressure into hydraulic pressure that the wheel cylinders use to press the brake pads against the rotors to bring the vehicle to a stop.
3. Brake Lines
Generally made of steel, brake lines are what carry the brake fluid from the master cylinder reservoir to the wheels where pressure is applied to stop the car.
4. Wheel Cylinders
The brake pads are connected to the wheel cylinders which either squeeze (disc brakes) or push apart (drum brakes) the brake pads when fluid flows into them.
5. Brake Pads
The brake pads are what actually rub against the drums or rotors. They are made of composite materials and designed to last for many, many thousands of miles. However, if you ever hear a grinding or howling noise when you try to stop your car it likely means it is time for new brake pads.
6. ABS Control Module
Found on vehicles with ABS brakes, the module performs diagnostic checks of the ABS braking system and determines when to send the correct pressure to each wheel to prevent the wheels from locking up.
7. Brake Booster
Reduces the amount of pressure needed for braking to allow any driver to operate the brakes. Uses engine vacuum and pressure to increase the force the brake pedal puts on the master cylinder.
8. Disc Brakes
Usually found on the front wheels, disc brakes feature brake pads that press against a disc (rotor) when the brake pedal is applied to stop the vehicle. The pads are attached to a brake calliper assembly that frames the rotor.
9. Drum Brakes
Located on the rear of the vehicle, drum brakes feature wheel cylinders, brake shoes and a brake drum. When the brake pedal is pressed, the brake shoes are forced into the brake drum by the wheel cylinders, bringing the vehicle to a stop.
10. Emergency Brake
Operates independently of the main brake system to keep the vehicle from rolling away. Also known as a parking brake, hand brake, and e-brake, the emergency brake is mainly used to keep the vehicle in place when parked.
11. Wheel Speed Sensors
Part of the ABS brake system, speed sensors monitor the speed of each tire and send the info to the ABS control module.
BRAKE OIL SPECIFIC CHARACTERISTICS
- Brake oil should be non-viscous (Low -Viscosity)
- It Should be in Compressible
- Its Boiling Point should be High Its Freezing Point Should be Low
- It Does Not React with the material of the pipe Through Which it passes
- It’s specific heat should be High
Brake Shoes Remade of a Special Type Of Material
- Iron nails and Particles
- Asbestos Dust
- Binding material
- Hardening Material
They are mixed together and given Desived a shape and size. after solidifying they are used as brake Shoes.
Classifications of brakes
For application
- (a) Foot Brake
- (b) Hand Brake
Concerning the Number of wheels:
- (a) Two- Wheel Brake
- (b) Four Wheel Brakes.
For the Brake Gear
- (a) Mechanical Brakes
- (b) Power Brakes
For the nature of power
- (a) Vacuum Brakes
- (b) Air Brakes
- (c) Hydraulic Brakes
- (d) Electric Brakes
With Respect to power unit
- (a) Direct Acting Brakes
- (b) Diaphragm brakes.
FAQ
Engine Parts Names| इंजन के पार्ट्स के नाम