Disc brakes System
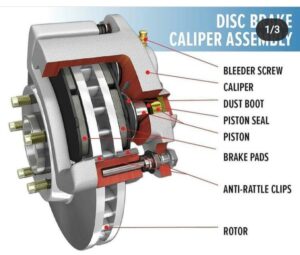
Disc brakes consist of a brake rotor that is attached directly to the wheel. Hydraulic pressure from the master cylinder causes a caliper (which holds the brake pads just outside the rotor) to squeeze the brake pads on either side of the rotor. The friction between the pads and the rotor causes the vehicle to slow and stop
Working Principle
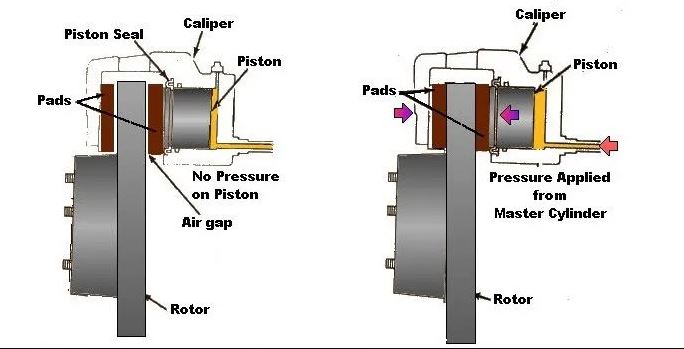
The working of a disc brake is based on Pascal law.
- When the brake pedal is pressed, the high pressure fluid from the master cylinder pushes the piston outward.
- The piston pushes the brake pad against the rotating disc.
- As the inner brake pad touches rotor, the fluid pressure exerts further force and the caliper moves inward and pulls the outward brake pad towards the rotating disc and it touches the disc.
- Now both the brake pads are pushes the rotating disc, a large amount of friction is generated in between the pads and rotating disc and slows down the vehicle and finally let it stop.
- When the brake pad is released, the piston moves inward, the brake pad moves away from the rotating disc. And the vehicle again starts to move.
The main components of a disc brake are:
- Wheel Hub: The disc rotor is attached to the wheel hub and it rotates with it. The wheel of the vehicle is bolted to the wheel hub.2. Caliper Assembly: The caliper assembly consist of(i) Brake pad: It makes contact with the rotor disc and due to the friction between the brake pad and rotor disc the vehicle speed reduces and it stops.
(ii) Caliper bracket
(iii) Caliper frame
(iv) Piston: It applies the brake force on the brake pads when brake lever is pressed.
(v) Slider pin: It is the sliding pin which slides in the hole when brake is applied.
(vi) Dust boots: It prevents the entry of dust into the caliper pin or slider pin hole.3. Disc Rotor: It is the rotating part of disc brake. When brakes are applied, a lot of heat is generated which can decrease the braking efficiency, so the rotor has drilled vent holes on it which dissipates the heat
Disc Brakes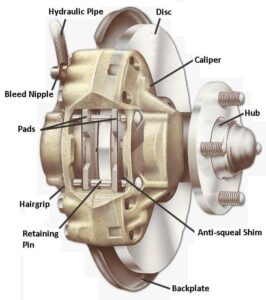
Usually found on the front wheels, disc brakes feature brake pads that press against a disc (rotor) when the brake pedal is applied to stop the vehicle. The pads are attached to a brake caliper assembly that frames the rotor.
Brake Pads
The brake pads are what actually rub against the drums or rotors. They are made of composite materials and designed to last for many, many thousands of miles. However, if you ever hear a grinding or howling noise when you try to stop your car it likely means it is time for new brake pads.
Advantages
- It is lighter than drum brakes.
- It has better cooling ( because the braking surface is directly exposed to the air)
- It offers better resistance to fade.
- It provides uniform pressure distribution
- The replacement of brake pads are easy.
- By design, they are self-adjusting brakes.
Disadvantages
- It is costlier than drum brakes.
- Higher pedal pressure is required for stopping the vehicle. This brake system is installed with a vacuum booster.
- No servo action is present.
- It is difficult to attach a suitable parking attachment
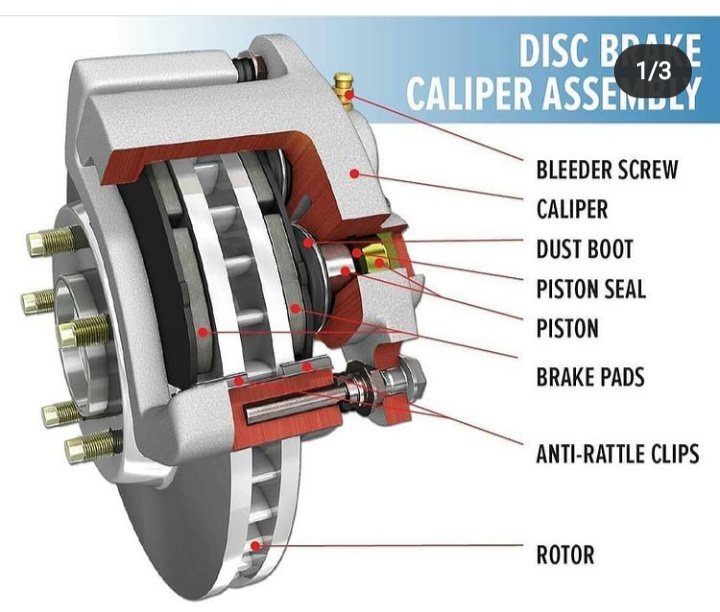
[…] Disc brakes System […]