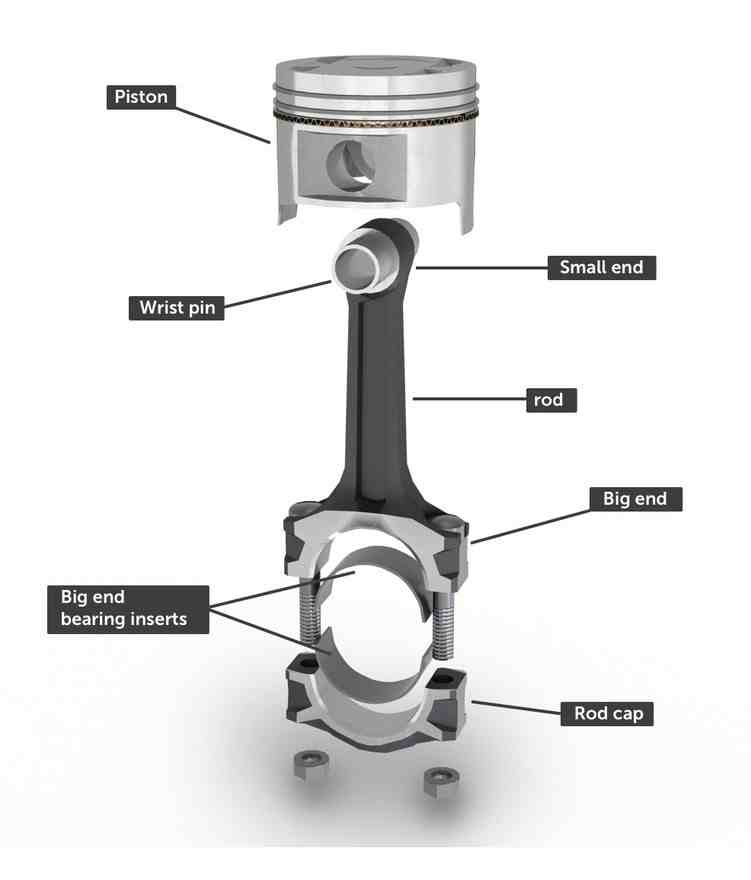
What is Piston and its function
Piston is the name of a part of the engine which keeps moving up and down inside the cylinder. The engine’s suction, compression, power and exhaust stroke are completed only by moving it up and down.
Piston is considered to be one of the most important parts in a reciprocating engine in which it helps to convert the chemical energy into the mechanical energy (Power).
Power is essentially a cylindrical plug that moves up and down in the cylinder. it is equipped with piston rings to provide a good seal between the cylinder wall and piston.
piston operate in the cylinder with minimum friction and should be able to withstand the high explosive force developed in the cylinder and also the very high temperature ranging From 2000 C to over 2800 C during operation
PISTON:-
- IT is moving component
- It compress air/Air-Fuel Mixture
- It work at high temperature environment
- It has to Force high pressure Developed time to Combustion of Fuel
- Piston generally mode up of :- Aluminum alloys, Cost Iron , Cast Steel, Chrome nickel.
- It is Treated with tin or Zinc oxide Called anodized
- Rigidly to withstand High pressure.
- Silence in Operation.
- To receive the Thrust Generated by the explain of the cylinder and transmit it to the connecting rod.
- To Reciprocate in the cylinder as a gas-tight plug causing suction, Compression, expansion and Exhaust Strokes.
The top of the piston is called head. ring grooves are cut on the circumference of the upper portion of the piston. the parts below the ring grooves is called skirt. the portions of the piston that separate the groove are called the lands. some pistons have a groove in the top land called a heat dam which reduced heat transfer to the rings. the piston bosses are the reinforced section of the piston designed to hold the piston pin or wrist pin.
Piston Material
the material used for piston is mainly aluminum alloy.. the heat conductivity of aluminum is about three times that of cast iron, and this combined with the greater thickness necessary for strength, enables an aluminum alloy piston to run at much lower temperature than cost iron
Piston Clearance
Piston clearance is the Distance Between the cylinder wall and the skirt the skirt is the lower part of the piston. the piston clearance is usually between 0.001 and 0.004 inch . in a running engine
,
the piston and ring move on film of oil that fill the piston clearance. it the clearance is too small , there is loss of power from high friction and severe wear. the piston shift from one side of the cylinder to the other with sufficient force to disappears. in order that fixed clearance may be used without risk of seizure
Expansion control in Piston
During operation the piston runs many degrees hotter than the cylinder because the cylinder is surrounding by cooling water. hence the piston expands more than the cylinder. this expansion must be controlled in order to avoid lass of adequate piston clearance such a loss may cause serious engine trouble. the problem is more accurate with aluminium piston because aluminium expands more rapidly than iron with the rise of temperature. the expansion of piston skirt can be controlled by several methods as follows:
- By keeping heat away from the lower part of the piston as much as possible
- By making heat dam:- Hat dam consists of a groove cut near the top of the piston. this reduces the size of the path the heat can travel the piston head to the skirt, therefore runs cooler and does not expand so much.
- By cam grinding the piston. the piston are finished so that they are slightly oval (elliptical) when cold
- By Using struts. the piston expansion may also be controlled by using the struts bands or belt cast into the piston. these couse the outward thrust of the expanding piston head to be carried more toward the piston- pin bosses than the thrust faces so that the effect is similar to that of the cam-ground pistons
Piston Head Shape
the piston head is often flat but may be shaped to suit the combution chamber. the ombustion space can be controlled by dishing or doming the piston crown and recess for the valve heads can also be machined into the crown. the compression ratio can be more accurately controlled by machining the combustion chamber in the piston, but it means that of the heat of combustion has to be dissipated through the piston instead of the of the cylinder head.
Piston PIN BOSS or Wrest PIN BOSS
piston pin or wrist pin or gudgeon pin connects the piston and the small end of the connecting rod.
Pins are usually hollow and made of alloy steel Their construction provides maximum strength with minimum weight. the piston pin bass and the combustion bowl lip are the piston area with the highest mechanical loads in direct injection turbocharged pin basses there are two different possible location for fatigue cracks one occurs a short Distance from the inner upper edge of the pin bore. cracks starting there are two halves. the second crack prone area is in a horizontal plane between the piston pin bore and the crown underside. this crack is more common if there is a small radius between crown and pin boss
The piston pin -also known as the gudgeon pin- transfers the entire generated power out of the combustion process from the piston, via the connecting rod down to the crankshaft. Due to the fact that the piston pin does not rotate, he is the engine component that have to withstand the highest stresses in engine operation. The piston pin connects the piston and the connecting rod and must withstand extremely high loads in changing directions. It is commonly made out of case-hardening or nitraded steel with a hardened, smooth ground and polished surface.
Piston Rings
- To provide a pressure seal to prevent blow by of burnt gases .
- To From the main path for conduction of heat from the piston crown to the cylinder walls.
- To Control the Flow of oil to the skirt and rings themselves in adequte Quantity
Piston Rings Material
material piston rings are usually made of fine-grained alloy cast iron. this material possess excellent heat and wear-resisting quantities inherent in its graphitec stucture. the elasticity of this material is also sufficient to impart radial expansion and compression which is necessary for assembly and removal of the ring, and particularly to enable it to exercise flexible pressure on the cylinder walls.
Types OF PISTON RINGS
There are two types of piston rings
- Compression Rings.
- Oil Control Rings.
- Compression Rings :- Compression Rings Fitted into the top grooves . The number of compression rings tend to increase the compression ration. Compression rings are usually made of cast iron . compression rings also help control oil.
- Oil Control Rings :- oil Control rings scrape off excessive oil from the cylinder all and return it to the oil pan. an oil control ring is fitted into the lower groove of the piston