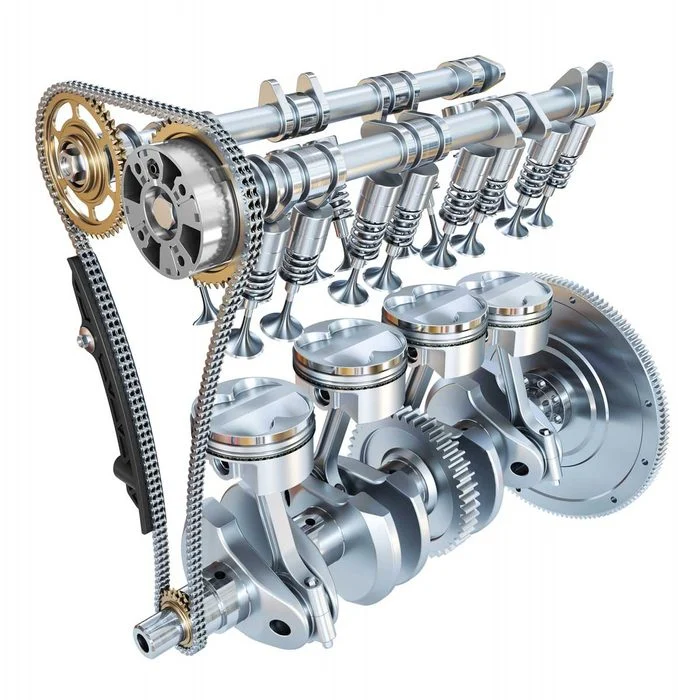
- In a diesel engine, the fuel is feed into the cylinder by a fuel injector and is mixed with air inside the cylinder. in a petrol engine, the air and petrol are mixed in the carburetor before they enter the cylinder.
- The diesel engine compressed only a charge of air and ignite ignition is accomplished by the heat of compression. The petrol engine compresses a mixture of air and petrol which is ignited by an electric spark.
- In a diesel engine, the compression is far above that used in petrol engine thus enabling it to convert more of the energy its fuel into work than does the petrol engine.
- the diesel engine burn fuels that Vaporize less readily than petrol and produces more kilometers per liter in a moto vehicle then does
- the petrol engine because of its higher thermal efficiency.
- diesel engine cylinder is fitted with a fuel injector petrol engine cylinder is fitted with a spark plug.
- diesel engine burn fuel of low volatility petrol engine burn fuel law of high
- diesel engine work on constant pressure Engine work on constant volume motorcycle
- diesel engine or adopt separately who is stationary and large marine use like tractors trucks locomotive and buses petrol engine are used in come paired with a light vehicle es like car jeep motor vehicle motorcycle scooter etc.
- In diesel engine the fuel consumption is less in comparison to petrol engine
- Running cost of diesel engine is less in comparison to petrol engine
- Diesel engine is heavier than the petrol engine
| Four- stroke Engine | Two stroke Engine |
| One working stroke for every two revolutions of the crankshaft. | one working stroke for each revolution of the crankshaft. |
| turning moment on the crankshaft is not even due to one working stroke for every two revolutions of the crankshaft. hence heavy flywheel is required and engine runs unbalanced . | turning moment on the crankshaft is more even due to one working stroke for each revolution of the crankshaft. hence lighter flywheel is required and engine runs balanced . |
| engine is heavy . | engine is light . |
| engine design is complicated. |
engine design is simple. |
| more cost. | more mechanical efficiency due to less friction on a few parts . |
| less mechanical efficiency due to more friction on many parts. | less output due to mixing of fresh charge with the burnt gases. |
| more output due to full fresh charge intake and full burnt gases exhaust. | engine runs hotter. |
| engine runs cooler. | engine is air cooled . |
| engine is water cooled. | more fuel consumption and fresh charge is mixed with exhaust gases. |
| less fuel consumption and full burning of fuel . | engine requires less space. |
| engine requires more space. | simple lubricating system. |
| complicated lubricating system. | engine creates more noise . |
| engine creates less noise. | use the mopeds scooter motor cycles. |
| used in cars buses trucks. | engine consist of inlet and exhaust ports . |
| engine consists of inlet and exhaust valves . | LESS thermal efficiency. |
| more thermal efficiency. | it consumes more lubricating oil. |
| it consumes less lubricating oil. | greater wear and tear of moving parts. |
Diesel Engine Cycle Working Process
the Diesel cycle differs from the Otto Cycle in one respect. In Diesel Cycle the Heat is added at constant Pressure Instead of at Constant Volume. The Air is Compressed in the Cylinder During the Compression Stroke From Point 1 to 2 . Now Heat is Added at constant Pressure From point 2 to3 and then the Air is expanded adiabatically From point 3 to 4 Finally the Heat is Rejected At Constant Volume From point 4 to 1 . the Air Returns to its Original Condition and the Cycle is complete.
- Adiabatic Compression 1-2
- Heat addition at Constant Pressure 2-3
- Adiabatic expansion 3-4
- Heat rejection at constant Volume 4-1
P:-Pressue V:- Specific Volumes What is a Diesel Engine?
What is a Diesel Engine? | IC Engine working process
In this post, we will learn about diesel engines, how a diesel engine works and what are its parts, we will also know about diesel cycle engines. When the fuel in the Internal Combustion Engine is ignited with the help of compressed air, then it is called Compression Ignition Engine or C.I Engine.
What is Diesel Engine?
A diesel engine uses diesel oil for its running. Diesel oil is light with low viscosity and high cetane number in a diesel engine. Only during the suction stroke, the air is sucked into the cylinder and the temperature also rises to about 1000F.
Diesel Engine Working process
Intake stroke or Suction stroke:-
- There is only air intake in this stroke
- In this, as soon as the engine starts, the piston moves down from the side of T.D.C to the bottom of B.D.C from the top, so that the pressure inside the cylinder is reduced and reduced. After this the intake valve opens and the air enters inside the cylinder. In this Piston goes from T.D.C to B.D.C.
- After that the valve closes.
Compression stroke
This stroke is called compression stroke because it contains compression of air. In the compression stroke, the piston moves from the bottom dead center to the top dead center. Due to which the piston compresses the air. In this, the pressure and temperature of the air increases due to compression. As the diesel is injected by the injector just before the stroke ends. Due to which the blast occurs inside the engine cylinder due to which high temperature is generated piston moves rapidly from T.D.C to B.D.C and during this stroke both the inlet and exhaust valves remain closed completely.
Expansion Stroke
As the diesel is injected by the injector just before the stroke ends. Due to which the blast occurs inside the engine cylinder due to which the high temperature is generated, the piston moves rapidly from T.D.C to B.D.C and during this stroke both the inlet and exhaust valves remain closed completely. Third stroke is working and power and expansion stroke – in this stroke hot gases are expanded and this puts hot gases pressure on piston and then due to this pressure piston moves from top dead center to bottom dead center which gives us this Work gets done in stroke. In this stroke both the inlet and exhaust valves remain closed. exhaust stroke
The fourth and last stroke is the exhaust stroke –
In this stroke the inlet valve remains closed and the valve remains open. The burnt gases in it come out from the engine cylinders in this stroke, in this the piston moves from bottom dead center to top dead center and removes the burnt gases which are left in the cylinder. As soon as the piston reaches the top dead center, the exhaust valve closes and the 4-stroke cycle is completed.
Difference between Diesel Engine And Petrol Engine
- In a diesel engine, the fuel is feed into the cylinder by a fuel injector and is mixed with air inside the cylinder. in a petrol engine, the air and petrol are mixed in the carburetor before they enter the cylinder.
- The diesel engine compressed only a charge of air and ignite ignition is accomplished by the heat of compression. The petrol engine compresses a mixture of air and petrol which is ignited by an electric spark.
- In a diesel engine, the compression is far above that used in petrol engine thus enabling it to convert more of the energy its fuel into work than does the petrol engine.
- the diesel engine burn fuels that Vaporize less readily than petrol and produces more kilometers per liter in a moto vehicle then does
- the petrol engine because of its higher thermal efficiency.
- diesel engine cylinder is fitted with a fuel injector petrol engine cylinder is fitted with a spark plug.
- diesel engine burn fuel of low volatility petrol engine burn fuel law of high
- diesel engine work on constant pressure Engine work on constant volume motorcycle
- diesel engine or adopt separately who is stationary and large marine use like tractors trucks locomotive and buses petrol engine are used in come paired with a light vehicle es like car jeep motor vehicle motorcycle scooter etc.
- In diesel engine the fuel consumption is less in comparison to petrol engine
- Running cost of diesel engine is less in comparison to petrol engine
- Diesel engine is heavier than the petrol engine
| Four- stroke Engine | Two stroke Engine |
| One working stroke for every two revolutions of the crankshaft. | one working stroke for each revolution of the crankshaft. |
| turning moment on the crankshaft is not even due to one working stroke for every two revolutions of the crankshaft. hence heavy flywheel is required and engine runs unbalanced . | turning moment on the crankshaft is more even due to one working stroke for each revolution of the crankshaft. hence lighter flywheel is required and engine runs balanced . |
| engine is heavy . | engine is light . |
| engine design is complicated. |
engine design is simple. |
| more cost. | more mechanical efficiency due to less friction on a few parts . |
| less mechanical efficiency due to more friction on many parts. | less output due to mixing of fresh charge with the burnt gases. |
| more output due to full fresh charge intake and full burnt gases exhaust. | engine runs hotter. |
| engine runs cooler. | engine is air cooled . |
| engine is water cooled. | more fuel consumption and fresh charge is mixed with exhaust gases. |
| less fuel consumption and full burning of fuel . | engine requires less space. |
| engine requires more space. | simple lubricating system. |
| complicated lubricating system. | engine creates more noise . |
| engine creates less noise. | use the mopeds scooter motor cycles. |
| used in cars buses trucks. | engine consist of inlet and exhaust ports . |
| engine consists of inlet and exhaust valves . | LESS thermal efficiency. |
| more thermal efficiency. | it consumes more lubricating oil. |
| it consumes less lubricating oil. | greater wear and tear of moving parts. |
Diesel Engine Cycle Working Process
the Diesel cycle differs from the Otto Cycle in one respect. In Diesel Cycle the Heat is added at constant Pressure Instead of at Constant Volume. The Air is Compressed in the Cylinder During the Compression Stroke From Point 1 to 2 . Now Heat is Added at constant Pressure From point 2 to3 and then the Air is expanded adiabatically From point 3 to 4 Finally the Heat is Rejected At Constant Volume From point 4 to 1 . the Air Returns to its Original Condition and the Cycle is complete.
- Adiabatic Compression 1-2
- Heat addition at Constant Pressure 2-3
- Adiabatic expansion 3-4
- Heat rejection at constant Volume 4-1
P:-Pressue V:- Specific Volumes What is a Diesel Engine?