Introduction
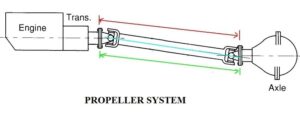
The propeller shaft, also known as the prop shaft or drive shaft, occupies a pivotal position in the transmission system of vehicles, serving as the conduit for transmitting torque between the gearbox and the differential. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of propeller shafts, exploring their various types, construction details, and operational mechanisms.
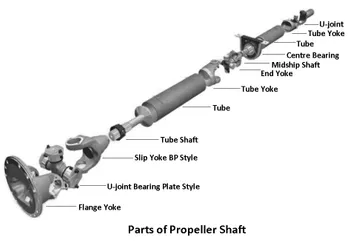
Propeller Shaft
- Propeller shafts, alternatively referred to as prop shafts or drive shafts, play a critical role in ensuring seamless power transmission within vehicles. These shafts, often composed of multiple segments interconnected by universal joints, facilitate the transfer of torque from the gearbox to the differential, ultimately driving the vehicle’s wheels. Constructed from durable materials such as steel, propeller shafts are meticulously engineered to withstand torsional stress while maintaining optimal balance to mitigate vibrations and whip at high speeds.
Propeller shaft diagram
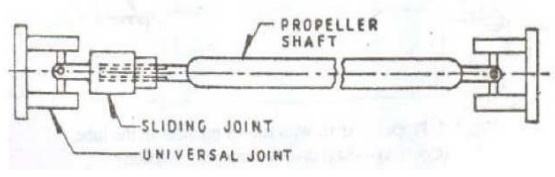
Types Propeller Shaft
-
Single-Piece Types Propeller shaft
-
Two-Piece Type Propeller shaft
- Single-Piece Propeller Shaft:
- A single-piece propeller shaft is a straightforward configuration where torque is transmitted directly to the differential through a continuous shaft.
- Two-Piece Propeller Shaft:
- Vehicles with extended wheelbases, such as trucks and buses, often utilize a two-piece propeller shaft design. This setup includes a center support bearing and an additional universal joint to enhance stability and prevent whipping action.
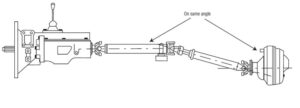 Avoid whipping action of a long shaft. a third universal joint between the two shaft and a center bearing to support the middle of the shaft assembly is provided
Avoid whipping action of a long shaft. a third universal joint between the two shaft and a center bearing to support the middle of the shaft assembly is provided
Shaft:-
As this has to withstand torsional load, it is usually made of tubular cross-section . it also has to be well balance to avoid whirling at high speed shafts are made of steel, aluminum or composite material.
U- Joint :-
A universal joint i used when two shafts are connected at an angle to transmit torque . in the transmission system of a moter vehicle the universal joint is used to connect the transmission main shaft and the propeller shaft and the differential pinion, shaft . A connecting joint that allows power to be transmitted between two rotating shaft at an angle to each other constant velocity universal joint and CV-joint
The universal joint may be three Types
- Cross-Types universal joint
- Ball and turning Types
- Constant Velocity Type
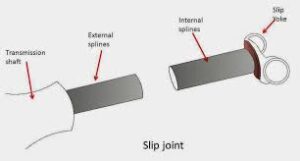
Slip Joint Or Sliding Joint :-
It is a increase and decrease a length of propeller shaft or drive shaft. In the drive train, a variable-length connection that permits the drive shaft to change its effective length
Construction Details:
Propeller shafts boast a tubular cross-section and are meticulously crafted to ensure structural integrity and durability. Reinforced with rubber-mounted bearings at the center, these shafts are engineered to absorb torsional forces and shocks effectively while resisting vibrations, thereby ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Operational Mechanisms:
The operational efficiency of propeller shafts hinges on the seamless interaction between various components, including universal joints and slip joints. Universal joints facilitate torque transmission between shafts at different angles, ensuring constant velocity and smooth operation. Meanwhile, slip joints enable the propeller shaft to adjust its length dynamically, accommodating changes in the vehicle’s drivetrain geometry and ensuring uninterrupted power transmission.